Getting Started¶
APIFairy is a minimalistic API framework for Flask with the following goals:
Give you a way to specify what the input arguments for each endpoint are, and automatically validate them for you.
Give you a way to specify what the response format for each endpoint is, and automatically serialize these responses for you.
Automatically generate API documentation for your project.
Introduce the least amount of rules. You should be able to code your endpoints in the style that you like.
Below you can see an example API endpoint augmented with APIFairy decorators:
from apifairy import authenticate, body, response, other_responses
# ...
@posts_blueprint.route('/posts/<int:id>', methods=['PUT'])
@authenticate(token_auth)
@body(update_post_schema)
@response(post_schema)
@other_responses({404: 'Post not found'})
def put(updated_post, id):
"""Edit a post."""
post = Post.query.get_or_404(id)
for attr, value in updated_post.items():
setattr(post, attr, value)
db.session.commit()
return post
APIFairy’s decorators are simple wrappers for existing solutions. In the
example above, token_auth is an intialized authentication object from the
Flask-HTTPAuth extension, and post_schema and update_post_schema are
Flask-Marshmallow schema objects. Using the decorator wrappers allow APIFairy
to automatically generate documentation using the OpenAPI 3.x standard. Below
is a screenshot of the documentation for the above endpoint:
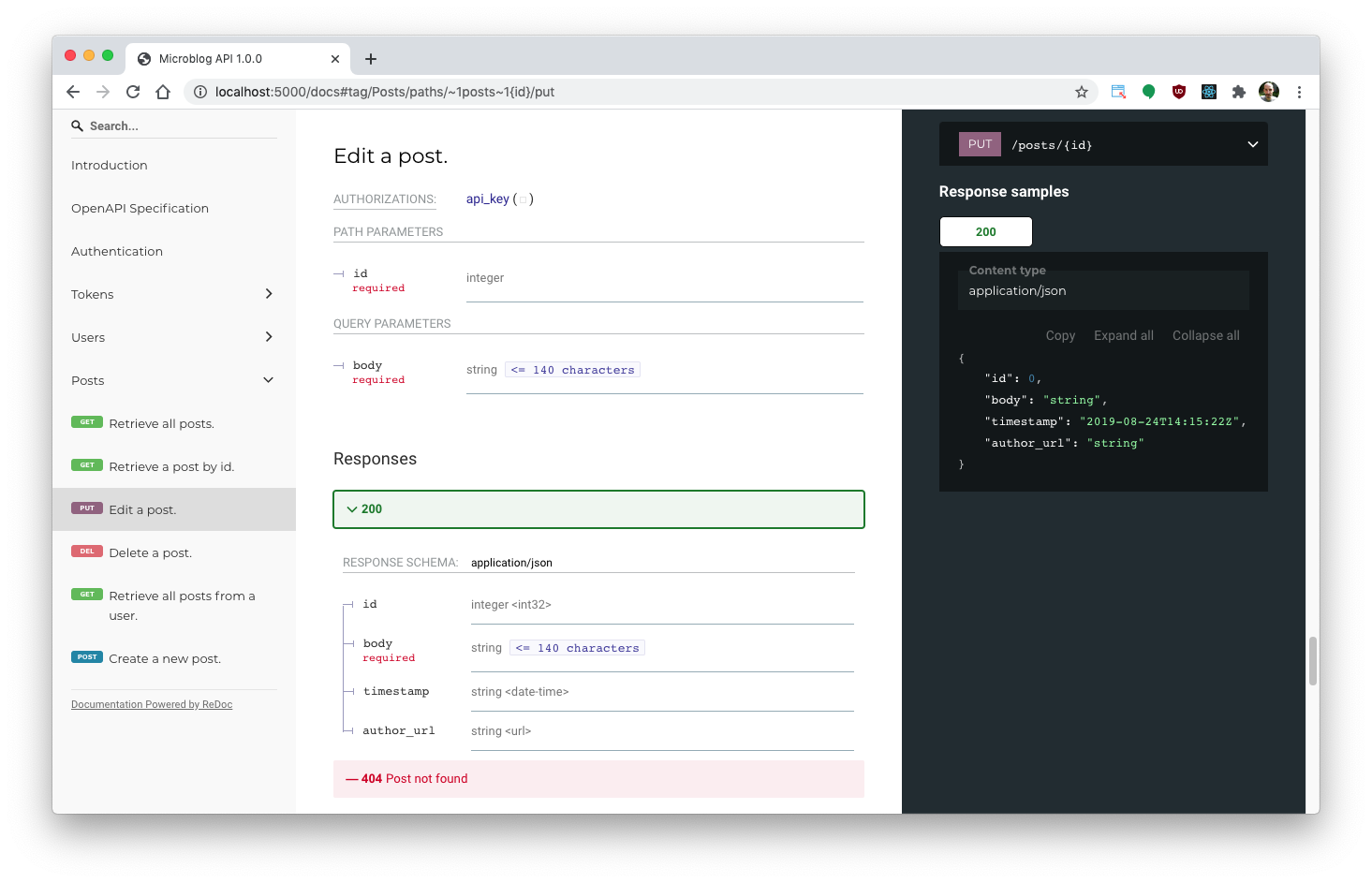
Installation¶
APIFairy is installed with pip:
pip install apifairy
Once installed, this package is initialized as a standard Flask extension:
from flask import Flask
from apifairy import APIFairy
app = Flask(__name__)
apifairy = APIFairy(app)
The two-phase initialization style is also supported:
from flask import Flask
from apifairy import APIFairy
apifairy = APIFairy()
def create_app():
app = Flask(__name__)
apifairy.init_app(app)
return app
Once APIFairy is initialized, automatically generated documentation can be accessed at the /docs URL. The raw OpenAPI documentation data in JSON format can be accessed at the /apispec.json URL. Both URLs can be changed in the configuration if desired.
Configuration¶
APIFairy imports its configuration from the Flask configuration object. The available options are shown in the table below.
Name |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
String |
No title |
The API’s title. |
|
String |
No version |
The API’s version. |
|
String |
/apispec.json |
The URL path where the JSON OpenAPI specification for this project is served. |
|
List |
[] |
A list of decorators to apply to the JSON OpenAPI endpoint. |
|
String |
redoc |
The documentation format to use. Supported formats are “redoc”, “swagger_ui”, “rapidoc” and “elements”. |
|
String |
/docs |
The URL path where the documentation is served. |
|
List |
[] |
A list of decorators to apply to the documentation endpoint. |
|
List |
|
A list of tags to include in the documentation, in the desired order. |
Using a Custom Documentation Endpoint¶
APIFairy provides templates for a few popular open source OpenAPI documentation renderers:
swagger_ui: Swagger UIredoc: ReDocrapidoc: RapiDocelements: Elements
If neither of these work for your project, or if you would like to configure
any of these differently, you can set the APIFAIRY_UI_PATH to None in
the configuration to disable the default documentation endpoint, and then
implement your own.
The stock documentation options offered by this package are implemented as
Jinja2 templates, which you can view on GitHub.
To implement a custom documentation, just create an endpoint in your Flask
application and render your own template, using the
{{ url_for('apifairy.json') }} expression where your documentation
renderer needs the API specification URL.
Note
When using a custom documentation endpoint, the APIFAIRY_UI_PATH and
APIFAIRY_UI_DECORATORS configuration options are ignored.
While less useful, the JSON OpenAPI specification endpoint can also be
customized by setting the APIFAIRY_APISPEC_PATH configuration option to
None. If a custom version of this endpoint is used, then the documentation
endpoint must also be provided by the application.
